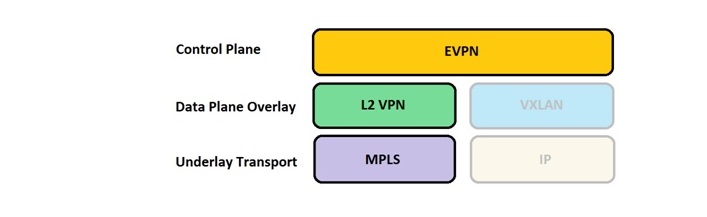
EVPN/MPLS vs VPLS
The aim of this post is to show a brief comparison of some key points for EVPN/MPLS and VPLS. You can see the details in the table below.
| Feature | EVPN/MPLS | VPLS |
| Use MPLS Transport | Yes | Yes |
| Protocol Evolution (Design Life) | Next Generation | Legacy |
| MPLS Fast Reroute (FRR) < 50ms | Yes | Yes |
| L2 Stretching | Yes | Yes |
| L3 Routing Integration | Yes, Integrated Routing andBridging (IRB). Single VPN technology for L3 and L2 VPNs. | No |
| VLAN Design | Flexible. Significant to the location. | Flat VLANs extended across locations can impact performance. |
| High Exposure to Broadcast Storms | No | Yes |
| DoS Attack Probability | Low | High |
| L2 PDUs must be tunnelled across MPLS Core, such as Spanning Tree (STP) BPDUs | No | Yes |
| Broadcast, Unknown Unicast and Multicast (BUM) Traffic | Suppression of BUM traffic at the PE device (locally). | Multicast and broadcast radiation to all sites. |
| MAC Address Learning | Control Plane (more efficient and scalable). | Data Plane (scalability considerations/limitations). |
| BGP to advertise MAC/IP info | Yes | No |
| Multi homing Active-Active per Flow | Yes | No |
| Multi homing Active-Standby per VLAN/Service | Yes | Yes |
| MAC Mobility | Yes | No |
| MAC Mass-Withdraw for fast convergence | BGP Based Withdraw. | LDP/BGP Based Withdraw. |
| Seamless VM Mobility | Yes | No |
| QoS Support | Yes | Yes |